 Yu, Jiashing, et al. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(11), 3516-3526.
Yu, Jiashing, et al. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(11), 3516-3526.
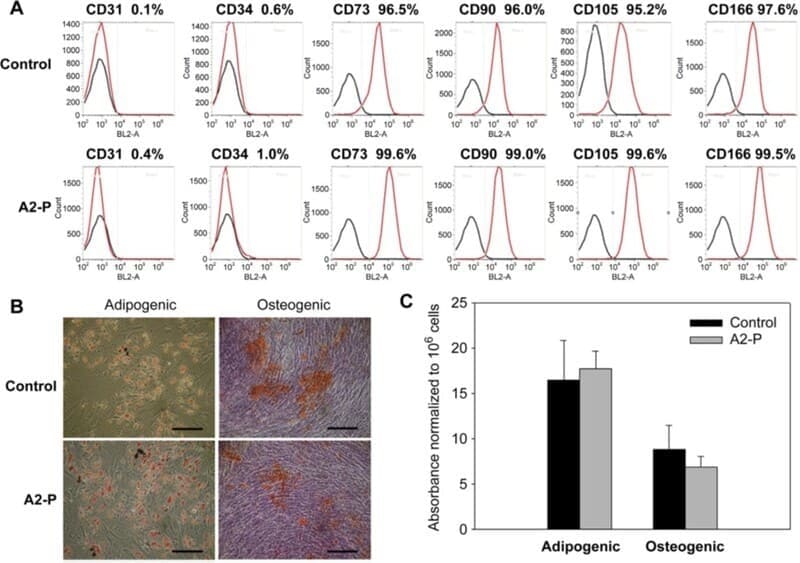
A stable form of ascorbic acid called ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (A2-P), was shown to dramatically increase the activity of fat stem cells (ASC) and produce ASC sheets to form in 7 days. Rich deposits of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) molecules, such as collagen, fibronectin, and laminin, are found in ASC sheets. During ASC sheet formation, A2-P further upregulates pluripotent genes, including Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog, by stimulating collagen synthesis. In summary, A2-P-mediated ASC sheet formation enhances the stemness and transdifferentiation capabilities of ASCs, thus representing a promising approach for regenerative medicine applications.
Cell sheet formation
Third passage ASCs were used for experiments. To make cell sheets, 5 × 10^5 ASCs were cultured for 7 days in a 100 mm culture dish. Culture medium was DMEM-HG with 10% FBS, 1% antibiotic-antimycotic and 250 μM A2-P. The control media had no A2-P. Each culture medium was changed every 2-3 days. Cells treated or not with A2-P were also analysed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), immunofluorescence and western blotting. An ERK1/2 inhibitor U0126 was dissolved in DMSO and tested for ERK1/2 inhibition assay. U0126 was in the 5 μM concentration, and did not affect APC proliferation in the pilot. ERK signaling was measured in the culture, and treated cells with A2-P or U0126 for 3 days.


 Yu, Jiashing, et al. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(11), 3516-3526.
Yu, Jiashing, et al. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(11), 3516-3526.
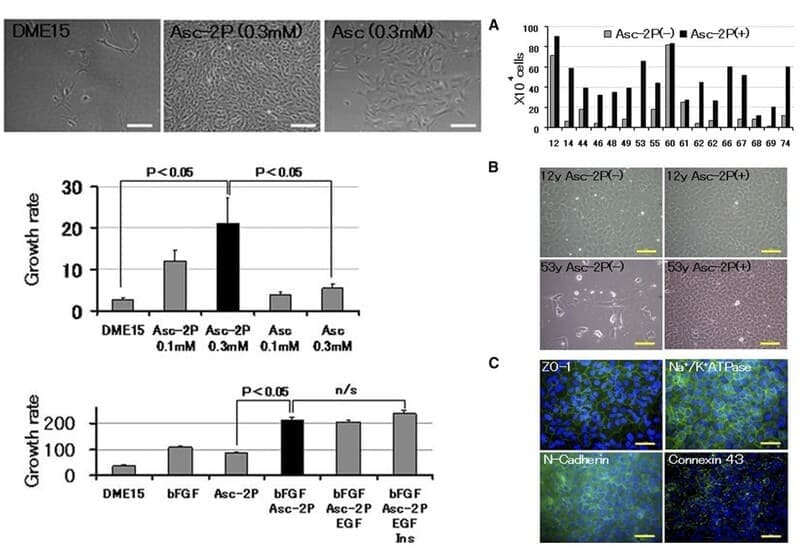 Shima, Nobuyuki, et al. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science, 2011, 52(12), 8711-8717.
Shima, Nobuyuki, et al. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science, 2011, 52(12), 8711-8717.